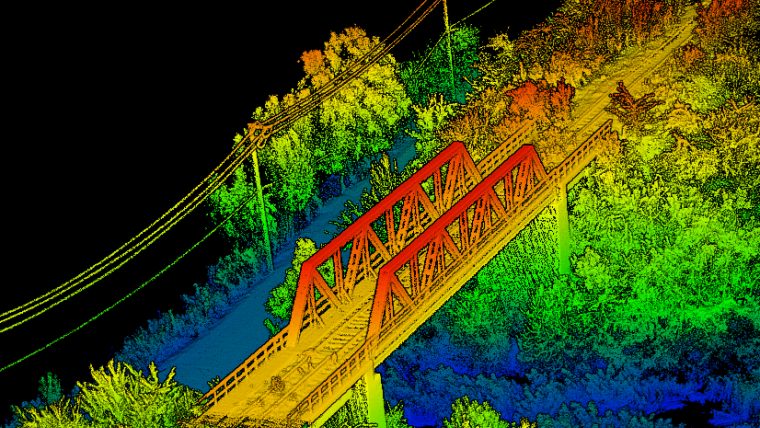
Let us introduce to you our first mini-serie on LiDARS.
LiDAR, short for light detection and ranging, is a technology which uses laser light to measure to distance between an object and an observer, forming a pixel-type view of the world known as a point cloud.
Here are multiple amazing applications related to this technology :
Virtual tours
LiDAR pulses can be used to create virtual 3D and 2D representations of an area, which can be used to create 360° and virtual tours, increasingly popular online.
Tourism and park management
LiDAR data is indispensable for tourism and park management; data analysis determines the best areas to use for various functions, such as where to build playgrounds, rides and footpaths.
Cancer image analysis
A hybrid LiDAR-radar system may be used for detecting the presence of objects, such as cancerous tumours, within tissues by detecting reflected signals from the tissue.
Mapping of wireless signal
LiDAR technology also has uses in wireless signal mapping, making it is easier to plan where each of the wireless transmitters will be positioned and to assess the strength and radius of the signal.
Gaming
Using LiDAR, you can digitally recreate any physical object, rendering detailed, accurate models in very little time. In gaming, this opens a world of possibilities, allowing developers to recreate entire cities and locations almost identical to the real world.
Archaeology
LiDAR has proved invaluable to archaeologists – such as the mapping of ancient Pompeii– helping them to plan field campaigns and observe patterns not visible from the ground. DEMs micro-topography hidden by trees and shrubs can also reveal with this technology.
Oil and gas exploration
Differential Absorption LiDAR offers a new method of oil and gas exploration. As well as being used to detect gases and particles, LiDAR mapping also provides an accurate 3D model of the terrain, minimising the project’s environmental impact.
Wind turbines
Scanning wind before it hits the wind turbine can help to maximise efficiency. LiDAR attached to the turbine itself is used to calculate the direction and strength of wind, and if will change the direction of the blade in order to generate more power.
At C2MI, we have everything you need to manufacture this type of technology. Interested?
Stay tuned to our second episode of this mini-series related to LiDar!